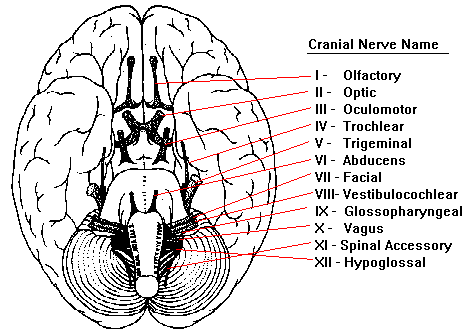
Patient Fact Sheet
Medical errors can occur anywhere in the health care system: In
hospitals, clinics, surgery centers, doctors' offices, nursing homes,
pharmacies, and patients' homes. Errors can involve medicines, surgery,
diagnosis, equipment, or lab reports. These tips tell what you can do to get
safer care.
One in seven Medicare patients in hospitals experience a medical error.
But medical errors can occur anywhere in the health care system: In hospitals,
clinics, surgery centers, doctors' offices, nursing homes, pharmacies, and
patients' homes. Errors can involve medicines, surgery, diagnosis, equipment,
or lab reports. They can happen during even the most routine tasks, such as
when a hospital patient on a salt-free diet is given a high-salt meal.
Most errors result from problems created by today's complex health care
system. But errors also happen when doctors* and patients have problems communicating. These tips tell what you can
do to get safer care.
What You Can Do to
Stay Safe
The best way you can help to prevent errors is to be an active member of
your health care team. That means taking part in every decision about your
health care. Research shows that patients who are more involved with their care
tend to get better results.
1. Make sure that
all of your doctors know about every medicine you are taking.
This includes prescription and over-the-counter medicines
and dietary supplements, such as vitamins and herbs.
2. Bring all of
your medicines and supplements to your doctor visits.
"Brown bagging" your medicines can help you and
your doctor talk about them and find out if there are any problems. It can also
help your doctor keep your records up to date and help you get better quality
care.
3. Make sure your
doctor knows about any allergies and adverse reactions you have had to
medicines.
This can help you to avoid getting a medicine that could
harm you.
4. When your
doctor writes a prescription for you, make sure you can read it.
If you cannot read your doctor's handwriting, your
pharmacist might not be able to either.
5. Ask for
information about your medicines in terms you can understand—both when your
medicines are prescribed and when you get them:
o What is the
medicine for?
o How am I supposed
to take it and for how long?
o What side effects
are likely? What do I do if they occur?
o Is this medicine
safe to take with other medicines or dietary supplements I am taking?
o What food, drink,
or activities should I avoid while taking this medicine?
6. When you pick
up your medicine from the pharmacy, ask: Is this the medicine that my doctor
prescribed?
7. If you have any
questions about the directions on your medicine labels, ask.
Medicine labels can be hard to understand. For example, ask
if "four times daily" means taking a dose every 6 hours around the
clock or just during regular waking hours.
8. Ask your
pharmacist for the best device to measure your liquid medicine.
For example, many people use household teaspoons, which
often do not hold a true teaspoon of liquid. Special devices, like marked
syringes, help people measure the right dose.
9. Ask for written
information about the side effects your medicine could cause.
If you know what might happen, you will be better prepared
if it does or if something unexpected happens.
Hospital Stays
10. If you are in a
hospital, consider asking all health care workers who will touch you whether
they have washed their hands.
Handwashing can prevent the spread of infections in
hospitals.
11. When you are
being discharged from the hospital, ask your doctor to explain the treatment
plan you will follow at home.
This includes learning about your new medicines, making sure
you know when to schedule follow-up appointments, and finding out when you can
get back to your regular activities.
It is important to know whether or not you should keep
taking the medicines you were taking before your hospital stay. Getting clear
instructions may help prevent an unexpected return trip to the hospital.
Surgery
11. If you are having
surgery, make sure that you, your doctor, and your surgeon all agree on exactly
what will be done.
Having surgery at the wrong site (for example, operating on
the left knee instead of the right) is rare. But even once is too often. The
good news is that wrong-site surgery is 100 percent preventable. Surgeons are
expected to sign their initials directly on the site to be operated on before
the surgery.
12. If you have a
choice, choose a hospital where many patients have had the procedure or surgery
you need.
Research shows that patients tend to have better results
when they are treated in hospitals that have a great deal of experience with
their condition.
Other Steps
14. Speak up if you
have questions or concerns.
You have a right to question anyone who is involved with
your care.
15. Make sure that
someone, such as your primary care doctor, coordinates your care.
This is especially important if you have many health problems
or are in the hospital.
16. Make sure that
all your doctors have your important health information.
Do not assume that everyone has all the information they
need.
17. Ask a family
member or friend to go to appointments with you.
Even if you do not need help now, you might need it later.
18. Know that
"more" is not always better.
It is a good idea to find out why a test or treatment is
needed and how it can help you. You could be better off without it.
19. If you have a
test, do not assume that no news is good news.
Ask how and when you will get the results.
20. Learn about your
condition and treatments by asking your doctor and nurse and by using other
reliable sources.
For example, treatment options based on the latest
scientific evidence are available from the Effective Health Care Web site. Ask
your doctor if your treatment is based on the latest evidence.